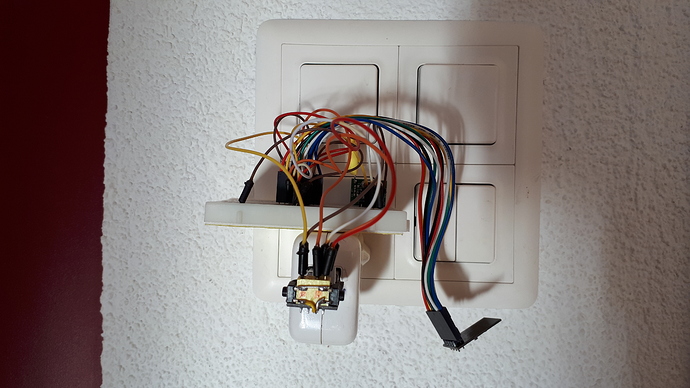
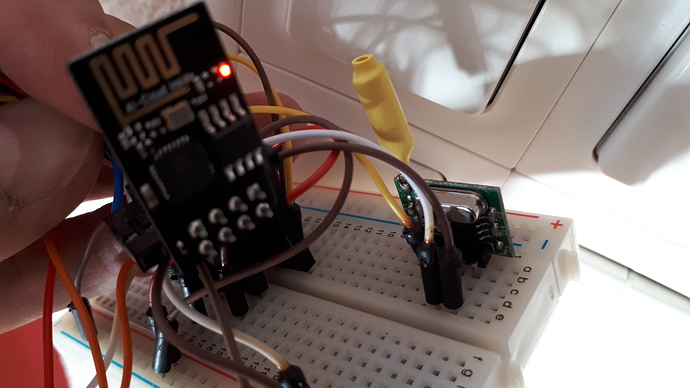
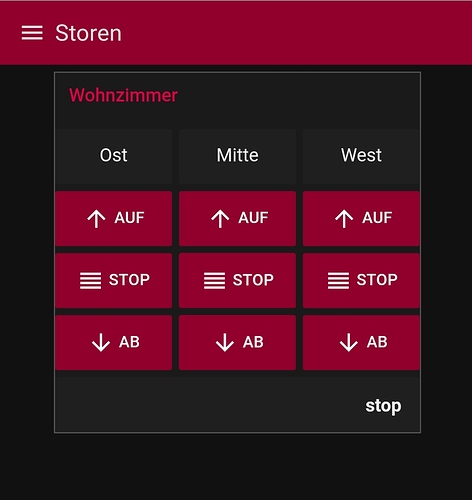
Sketch mit EEPROM und MQTT:
/* This sketch allows you to emulate a Somfy RTS or Simu HZ remote.
If you want to learn more about the Somfy RTS protocol, check out Somfy Smoove Origin RTS Protocol | PushStack
The rolling code will be stored in EEPROM, so that you can power the Arduino off.
Easiest way to make it work for you:
- Choose a remote number
- Choose a starting point for the rolling code. Any unsigned int works, 1 is a good start
- Upload the sketch
- Long-press the program button of YOUR ACTUAL REMOTE until your blind goes up and down slightly
- send 'p' to the serial terminal
To make a group command, just repeat the last two steps with another blind (one by one)
Then:
- m, u or h will make it to go up
- s make it stop
- b, or d will make it to go down
- you can also send a HEX number directly for any weird command you (0x9 for the sun and wind detector for instance)
*/
/* Motor 1 Rollingcode >31 Remote 0x521370
Motor 3 Rollingcode >72 Remote 0x521373
Motor 4 Rollingcode >274 Remote 0x521374
*/
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include "Adafruit_MQTT.h"
#include "Adafruit_MQTT_Client.h"
#include "EEPROM.h"
extern "C" {
#include "user_interface.h"
}
/************************* SOMFY Settings *********************************/
#define TXP 0 //DAT PIN of RFChip
#define SYMBOL 640
#define HAUT 0x2 //UP
#define STOP 0x1 //MY
#define BAS 0x4 //DOWN
#define PROG 0x8 //PROG
#define REMOTE 0x521373 //<-- Change it!
/************************* WiFi Access Point *********************************/
#define WLAN_SSID "SSID"
#define WLAN_PASS "PASS"
/************************* MQTT Settings *********************************/
#define AIO_SERVER "homegear.local"
#define AIO_SERVERPORT 1883 // use 8883 for SSL
#define AIO_USERNAME ""
#define AIO_KEY ""
/************ Global State (you don't need to change this!) ******************/
// Create an ESP8266 WiFiClient class to connect to the MQTT server.
WiFiClient client;
// or... use WiFiClientSecure for SSL
//WiFiClientSecure client;
// Setup the MQTT client class by passing in the WiFi client and MQTT server and login details.
Adafruit_MQTT_Client mqtt(&client, AIO_SERVER, AIO_SERVERPORT, AIO_USERNAME, AIO_USERNAME, AIO_KEY);
/****************************** Feeds ***************************************/
// Notice MQTT paths for AIO follow the form: <username>/feeds/<feedname>
// Setup a feed for Subscription
Adafruit_MQTT_Subscribe storen = Adafruit_MQTT_Subscribe(&mqtt, "wohnzimmer/storen/mitte");
void MQTT_connect();
unsigned int newRollingCode = 1; //<-- Change it!
unsigned int rollingCode = 72;
byte frame[7];
byte checksum;
void BuildFrame(byte *frame, byte button);
void SendCommand(byte *frame, byte sync);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(500);
EEPROM.begin(512);
// EEPROM.write(0,0); // RollingCode manuell anpassen high byte
// EEPROM.write(1,59); // RollingCode manuell anpassen low byte
// EEPROM.commit();
Serial.print("EEPROM Wert = ");
Serial.print(EEPROM.read(0));
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(EEPROM.read(1));
// Connect to WiFi access point.
Serial.println(); Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(WLAN_SSID);
wifi_station_set_hostname("somfy");
WiFi.begin(WLAN_SSID, WLAN_PASS);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.print("IP address: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.print("Hostname: "); Serial.println(WiFi.hostname());
// Setup MQTT subscription for storen.
mqtt.subscribe(&storen);
pinMode(TXP, OUTPUT);; // Pin DAT
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW); // LOW
if (rollingCode < newRollingCode) {
rollingCode = newRollingCode;
}
byte high = EEPROM.read(0); //read the first half
byte low = EEPROM.read(1); //read the second half
rollingCode = (high << 8) + low; //reconstruct the integer
//rollingCode = EEPROM.read(0); //EEPROM Auslesen
Serial.print("Simulated remote number : "); Serial.println(REMOTE, HEX);
Serial.print("Current rolling code : "); Serial.println(rollingCode);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char serie = (char)Serial.read();
Serial.println("");
// Serial.print("Remote : "); Serial.println(REMOTE, HEX);
if (serie == 'm' || serie == 'u' || serie == 'h') {
Serial.println("Monte"); // Somfy is a French company, after all.
BuildFrame(frame, HAUT);
}
else if (serie == 's') {
Serial.println("Stop");
BuildFrame(frame, STOP);
}
else if (serie == 'b' || serie == 'd') {
Serial.println("Descend");
BuildFrame(frame, BAS);
}
else if (serie == 'p') {
Serial.println("Prog");
BuildFrame(frame, PROG);
}
else {
Serial.println("Custom code");
BuildFrame(frame, serie);
}
Serial.println("");
SendCommand(frame, 2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
SendCommand(frame, 7);
}
}
// Ensure the connection to the MQTT server is alive (this will make the first
// connection and automatically reconnect when disconnected). See the MQTT_connect
// function definition further below.
MQTT_connect();
// this is our 'wait for incoming subscription packets' busy subloop
// try to spend your time here
Adafruit_MQTT_Subscribe *subscription;
while ((subscription = mqtt.readSubscription(5000))) {
// Check if its the storen feed
if (subscription == &storen) {
Serial.print(F("MQTT Storen: "));
Serial.println((char *)storen.lastread);
if (strcmp((char *)storen.lastread, "up") == 0) {
BuildFrame(frame, HAUT);
}
if (strcmp((char *)storen.lastread, "stop") == 0) {
BuildFrame(frame, STOP);
}
if (strcmp((char *)storen.lastread, "down") == 0) {
BuildFrame(frame, BAS);
}
Serial.println(" fire!");
SendCommand(frame, 2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
SendCommand(frame, 7);
}
}
}
// ping the server to keep the mqtt connection alive
// NOT required if you are publishing once every KEEPALIVE seconds
if (! mqtt.ping()) {
mqtt.disconnect();
}
}
// Function to connect and reconnect as necessary to the MQTT server.
// Should be called in the loop function and it will take care if connecting.
void MQTT_connect() {
int8_t ret;
// Stop if already connected.
if (mqtt.connected()) {
return;
}
Serial.print("Connecting to MQTT... ");
uint8_t retries = 3;
while ((ret = mqtt.connect()) != 0) { // connect will return 0 for connected
Serial.println(mqtt.connectErrorString(ret));
Serial.println("Retrying MQTT connection in 5 seconds...");
mqtt.disconnect();
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds
retries--;
if (retries == 0) {
// basically die and wait for WDT to reset me
while (1);
}
}
Serial.println("MQTT Connected!");
}
// Function to Build SOMFY RTS Frame
void BuildFrame(byte *frame, byte button) {
unsigned int code = rollingCode;
frame[0] = 0xA7; // Encryption key. Doesn't matter much
frame[1] = button << 4; // Which button did you press? The 4 LSB will be the checksum
frame[2] = code >> 8; // Rolling code (big endian)
frame[3] = code; // Rolling code
frame[4] = REMOTE >> 16; // Remote address
frame[5] = REMOTE >> 8; // Remote address
frame[6] = REMOTE; // Remote address
Serial.print("Frame : ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
if (frame[i] >> 4 == 0) { // Displays leading zero in case the most significant
Serial.print("0"); // nibble is a 0.
}
Serial.print(frame[i], HEX); Serial.print(" ");
}
// Checksum calculation: a XOR of all the nibbles
checksum = 0;
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
checksum = checksum ^ frame[i] ^ (frame[i] >> 4);
}
checksum &= 0b1111; // We keep the last 4 bits only
//Checksum integration
frame[1] |= checksum; // If a XOR of all the nibbles is equal to 0, the blinds will
// consider the checksum ok.
Serial.println(""); Serial.print("With checksum : ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
if (frame[i] >> 4 == 0) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(frame[i], HEX); Serial.print(" ");
}
// Obfuscation: a XOR of all the bytes
for (byte i = 1; i < 7; i++) {
frame[i] ^= frame[i - 1];
}
Serial.println(""); Serial.print("Obfuscated : ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
if (frame[i] >> 4 == 0) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(frame[i], HEX); Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Rolling Code : "); Serial.println(rollingCode);
rollingCode = rollingCode + 1;
// We store the value of the rolling code in the EEPROM. It should take up to 2 adresses but the
EEPROM.write(0, highByte(rollingCode)); //write the first half
EEPROM.write(1, lowByte(rollingCode)); //write the second half
Serial.print("Write EEPROM Adr 0 : "); Serial.println(highByte(rollingCode));
Serial.print("Write EEPROM Adr 1 : "); Serial.println(lowByte(rollingCode));
EEPROM.commit(); // Arduino function takes care of it.
}
// Function to Send SOMFY RTS Command
void SendCommand(byte *frame, byte sync) {
if (sync == 2) { // Only with the first frame.
//Wake-up pulse & Silence
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(9415);
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(89565);
}
// Hardware sync: two sync for the first frame, seven for the following ones.
for (int i = 0; i < sync; i++) {
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(4 * SYMBOL);
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(4 * SYMBOL);
}
// Software sync
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(4550);
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
//Data: bits are sent one by one, starting with the MSB.
for (byte i = 0; i < 56; i++) {
if (((frame[i / 8] >> (7 - (i % 8))) & 1) == 1) {
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
}
else {
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
}
}
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(30415); // Inter-frame silence
}
Obenstehendes Sketch hat mal funktioniert, dann habe ich mich an das Schrieben des aktuellen Rollingcodes ins Eeprom gewagt. Problematisch wurde dann, ich möchte mehrere Motoren ansteuern können, heisst, ich muss wissen welchen REMOTE ID ich verwende und wo gerade derren ROLLINGCODE steht.
Um dies zu vereinfachen, habe ich dann mal das ganze MQTT Gedöns rauschgelöscht und das nachfolgende Sketch geschrieben. Das ist gut ein halbes Jahr her, somit weiss ich gerade nicht mehr, was davon funktioniert hat.
Wichtig zu wissen: Das Ganze wollte ich auf einem ESP-01 zum Fliegen bringen, damit ich direkt aus Node-red via MQTT auf RTS kann. ESP-01 unterstützt jedoch nicht die einfachen EEPROM Operationen des Arduino. Somit würde ich wohl beim nächsten Versuch auf einen Arduino Nano wechseln und diesen via I2C, UART oder GPIO mit Node-red und Homegear ansteuern, doch man beachte die kurze Reichweite, solange man noch mit 433.92 MHz funkt!
Sketch mit EEPROM ohne MQTT
/* This sketch allows you to emulate a Somfy RTS or Simu HZ remote.
If you want to learn more about the Somfy RTS protocol, check out https://pushstack.wordpress.com/somfy-rts-protocol/
The rolling code will be stored in EEPROM, so that you can power the Arduino off.
Easiest way to make it work for you:
- Choose a remote number
- Choose a starting point for the rolling code. Any unsigned int works, 1 is a good start
- Upload the sketch
- Long-press the program button of YOUR ACTUAL REMOTE until your blind goes up and down slightly
- send 'p' to the serial terminal
To make a group command, just repeat the last two steps with another blind (one by one)
Then:
- m, u or h will make it to go up
- s make it stop
- b, or d will make it to go down
- you can also send a HEX number directly for any weird command you (0x9 for the sun and wind detector for instance)
*/
/* Motor 1 Rollingcode >31 Remote 0x521370
Motor 3 Rollingcode >185 Remote 0x521373
Motor 4 Rollingcode >274 Remote 0x521374
*/
#include "EEPROM.h"
/************************* SOMFY Settings *********************************/
#define TXP 0 //DAT PIN of RFChip
#define SYMBOL 640
#define HAUT 0x2 //UP
#define STOP 0x1 //MY
#define BAS 0x4 //DOWN
#define PROG 0x8 //PROG
#define REMOTE 0x521373 //<-- Change it!
unsigned int newRollingCode = 185; //<-- Change it!
unsigned int rollingCode = 185;
byte frame[7];
byte checksum;
void BuildFrame(byte *frame, byte button);
void SendCommand(byte *frame, byte sync);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(500);
EEPROM.begin(512);
// EEPROM.write(0,0); // RollingCode manuell anpassen high byte
// EEPROM.write(1,59); // RollingCode manuell anpassen low byte
// EEPROM.commit();
byte high = EEPROM.read(0); //read the first half
byte low = EEPROM.read(1); //read the second half
rollingCode = (high << 8) + low; //reconstruct the integer
//rollingCode = EEPROM.read(0); //EEPROM Auslesen
Serial.print("EEPROM Wert = ");
Serial.print(high);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(low);
pinMode(TXP, OUTPUT);; // Pin DAT
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW); // LOW
if (rollingCode < newRollingCode) {
rollingCode = newRollingCode;
}
Serial.print("Simulated remote number : "); Serial.println(REMOTE, HEX);
Serial.print("Current rolling code : "); Serial.println(rollingCode);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char serie = (char)Serial.read();
Serial.println("");
// Serial.print("Remote : "); Serial.println(REMOTE, HEX);
if (serie == 'm' || serie == 'u' || serie == 'h') {
Serial.println("Monte"); // Somfy is a French company, after all.
BuildFrame(frame, HAUT);
}
else if (serie == 's') {
Serial.println("Stop");
BuildFrame(frame, STOP);
}
else if (serie == 'b' || serie == 'd') {
Serial.println("Descend");
BuildFrame(frame, BAS);
}
else if (serie == 'p') {
Serial.println("Prog");
BuildFrame(frame, PROG);
}
else {
Serial.println("Custom code");
BuildFrame(frame, serie);
}
Serial.println("");
SendCommand(frame, 2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
SendCommand(frame, 7);
}
}
}
// Function to Build SOMFY RTS Frame
void BuildFrame(byte *frame, byte button) {
unsigned int code = rollingCode;
frame[0] = 0xA7; // Encryption key. Doesn't matter much
frame[1] = button << 4; // Which button did you press? The 4 LSB will be the checksum
frame[2] = code >> 8; // Rolling code (big endian)
frame[3] = code; // Rolling code
frame[4] = REMOTE >> 16; // Remote address
frame[5] = REMOTE >> 8; // Remote address
frame[6] = REMOTE; // Remote address
Serial.print("Frame : ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
if (frame[i] >> 4 == 0) { // Displays leading zero in case the most significant
Serial.print("0"); // nibble is a 0.
}
Serial.print(frame[i], HEX); Serial.print(" ");
}
// Checksum calculation: a XOR of all the nibbles
checksum = 0;
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
checksum = checksum ^ frame[i] ^ (frame[i] >> 4);
}
checksum &= 0b1111; // We keep the last 4 bits only
//Checksum integration
frame[1] |= checksum; // If a XOR of all the nibbles is equal to 0, the blinds will
// consider the checksum ok.
Serial.println(""); Serial.print("With checksum : ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
if (frame[i] >> 4 == 0) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(frame[i], HEX); Serial.print(" ");
}
// Obfuscation: a XOR of all the bytes
for (byte i = 1; i < 7; i++) {
frame[i] ^= frame[i - 1];
}
Serial.println(""); Serial.print("Obfuscated : ");
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
if (frame[i] >> 4 == 0) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(frame[i], HEX); Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Rolling Code : "); Serial.println(rollingCode);
rollingCode = rollingCode + 1;
// We store the value of the rolling code in the EEPROM. It should take up to 2 adresses but the
EEPROM.write(0, highByte(rollingCode)); //write the first half
EEPROM.write(1, lowByte(rollingCode)); //write the second half
Serial.print("Write EEPROM Adr 0 : "); Serial.println(highByte(rollingCode));
Serial.print("Write EEPROM Adr 1 : "); Serial.println(lowByte(rollingCode));
EEPROM.commit(); // Arduino function takes care of it.
}
// Function to Send SOMFY RTS Command
void SendCommand(byte *frame, byte sync) {
if (sync == 2) { // Only with the first frame.
//Wake-up pulse & Silence
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(9415);
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(89565);
}
// Hardware sync: two sync for the first frame, seven for the following ones.
for (int i = 0; i < sync; i++) {
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(4 * SYMBOL);
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(4 * SYMBOL);
}
// Software sync
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(4550);
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
//Data: bits are sent one by one, starting with the MSB.
for (byte i = 0; i < 56; i++) {
if (((frame[i / 8] >> (7 - (i % 8))) & 1) == 1) {
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
}
else {
digitalWrite(TXP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(SYMBOL);
}
}
digitalWrite(TXP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(30415); // Inter-frame silence
}
Die Diskussion ist eröffnet …
 - habe ich mich hier wohl etwas zu kurz gefasst.
- habe ich mich hier wohl etwas zu kurz gefasst.